Photovoltaic (Solar Electric)
Photovoltaic (PV) devices generate electricity directly from sunlight via an electronic process that occurs naturally in certain types of material, called semiconductors. Electrons in these materials are freed by solar energy and can be induced to travel through an electrical circuit, powering electrical devices or sending electricity to the grid.
PV devices can be used to power anything from small electronics such as calculators and road signs up to homes and large commercial businesses.
Related Resources
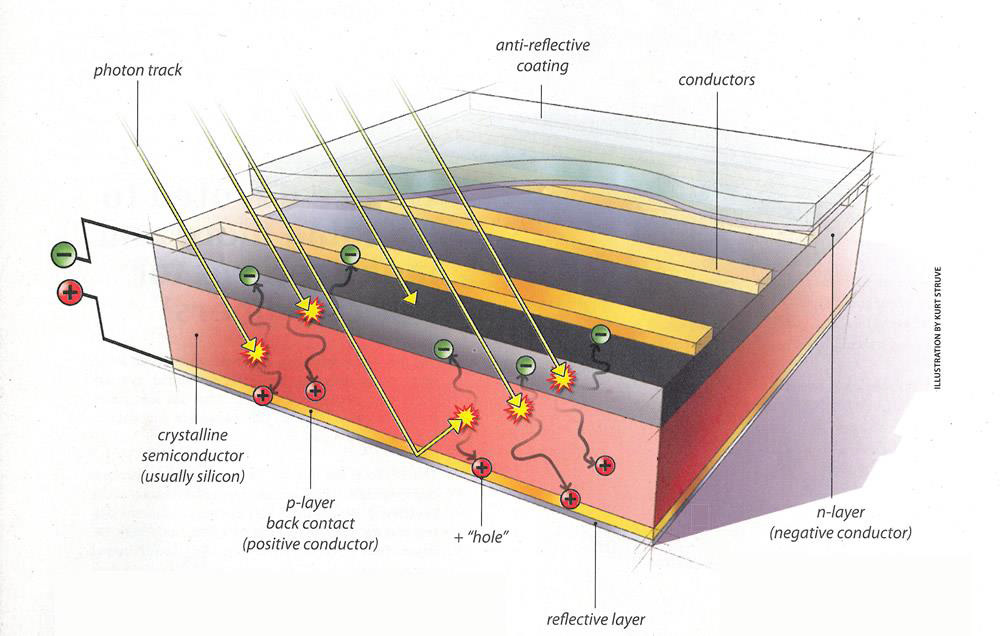
How does PV technology work?Photons strike and ionize semiconductor material on the solar panel, causing outer electrons to break free of their atomic bonds. Due to the semiconductor structure, the electrons are forced in one direction creating a flow of electrical current.
Related Resources
- PRESENTATION - Solar Photovoltaic Technology
- REPORT - Residential Photovoltaic Installations Increase Home Value in California
How does PV technology work?Photons strike and ionize semiconductor material on the solar panel, causing outer electrons to break free of their atomic bonds. Due to the semiconductor structure, the electrons are forced in one direction creating a flow of electrical current.
Diagram of a typical crystalline silicon solar cell. To make this type of cell, wafers of high-purity silicon are “doped” with various impurities and fused together. The resulting structure creates a pathway for electrical current within and between the solar cells.
History of Photovoltaic Technology
The PV effect was observed as early as 1839 by Alexandre Edmund Becquerel, and was the subject of scientific inquiry through the early twentieth century. In 1954, Bell Labs in the U.S. introduced the first solar PV device that produced a useable amount of electricity, and by 1958, solar cells were being used in a variety of small-scale scientific and commercial applications.
The energy crisis of the 1970s saw the beginning of major interest in using solar cells to produce electricity in homes and businesses, but prohibitive prices (nearly 30 times higher than the current price) made large-scale applications impractical.
Industry developments and research in the following years made PV devices more feasible and a cycle of increasing production and decreasing costs began which continues even today.
Industry developments and research in the following years made PV devices more feasible and a cycle of increasing production and decreasing costs began which continues even today.
Costs of Solar Photovoltaics
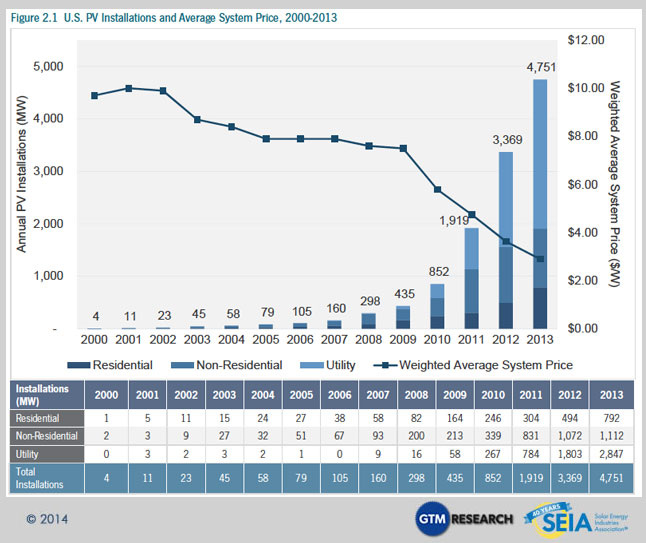
Rapidly falling prices have made solar more affordable than ever. The average price of a completed PV system has dropped by 33 percent since the beginning of 2011.
Modern Photovoltaics The cost of PV has dropped dramatically as the industry has scaled up manufacturing and incrementally improved the technology with new materials. Installation costs have come down too with more expereinced and trained installers. However, the U.S. still remains behind other nations that have stronger national policies to shift energy use from fossil fuels to solar. Globally, the U.S. is the fourth largest market for PV installations behind world leaders Germany, Japan and Spain.
Most modern solar cells are made from either crystalline silicon or thin-film semiconductor material. Silicon cells are more efficient at converting sunlight to electricity, but generally have higher manufacturing costs. Thin-film materials typically have lower efficiencies, but can be simpler and less costly to manufacture. A specialized category of solar cells - called multi-junction or tandem cells - are used in applications requiring very low weight and very high efficiencies, such as satellites and military applications. All types of PV systems are widely used today in a variety of applications.
Most modern solar cells are made from either crystalline silicon or thin-film semiconductor material. Silicon cells are more efficient at converting sunlight to electricity, but generally have higher manufacturing costs. Thin-film materials typically have lower efficiencies, but can be simpler and less costly to manufacture. A specialized category of solar cells - called multi-junction or tandem cells - are used in applications requiring very low weight and very high efficiencies, such as satellites and military applications. All types of PV systems are widely used today in a variety of applications.